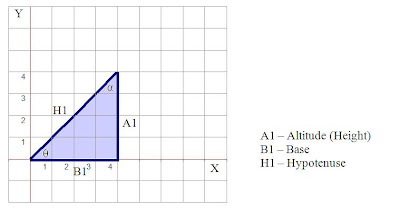
It is a right angled triangle, since one of the angles is 90 degrees.
It has two more angles, alpha (α) and theta (θ).
Now take the ratio of side A and side H.
Increase the size of B, H and A such that the angles inside remain constant.
Now take the ratio of side A1 and side H1. We can see that the ratio is same.
A1/H1 = A2/H2
Similarly the ratio of side B to side H of both triangles will also be constant.
i.e. B1/H1 = B2/H2
But if we change the angle theta and alpha then this ratio will not be the same.
The triangles which we considered were a right angled triangle.
What we found out is that in a right angled triangle the ratio of sides are dependent on the angles α and θ. This ratio is not dependent on the length of the sides.
So for a right angled triangle, we can easily create ratios for any of the angles. But for a triangle the angle theta can vary from 0 to 90 only.
This ratio is what is defined as sine and cosine
Sine is the ratio of opposite side to the hypotenuse
Cosine is the ratio of adjacent side to hypotenuse
For finding the sine value, we can refer to the logarithm table or
Simply draw a right angled triangle which contains the angle, whose sine is to be calculated and find out the ratio of opposite side and hypotenuse.
When theta is 0
Sin 0 = Opposite side/ Hypotenuse
= 0/Hypotenuse (since angle 0 means the hypotenuse and base of triangle overlap each other and the height from edge of base to edge of hypotenuse is 0.
= 0
Cos 0 = Adjacent side/Hypotenuse
= 1
Since in this case both the adjacent side and hypotenuse will be of the same size. Only one of its case. In no other angles will the adjacent side be equal to hypotenuse. Similarly for any angle θ, the ratio can be calculated as shown below.
What is the unit of sine and cosine?
From the above description we can see that both sine and cosine are ratios. They are ratios of two lengths. Hence the units cancel each other and they are unitless.
So the points to note are
In a right angled triangle
- For any value of θ
- - The ratio of adjacent side to Hypotenuse (SINE)
- - - The ratio of opposite side to Hypotenuse (COSINE)
- - - - IS A CONSTANT
Sin θ and Cos θ is not depended on the length of the sides
How this knowledge helps in study of Electronics?
This will be dealt in next post.




